Potential uses for
stem cells. (Blog post #2)
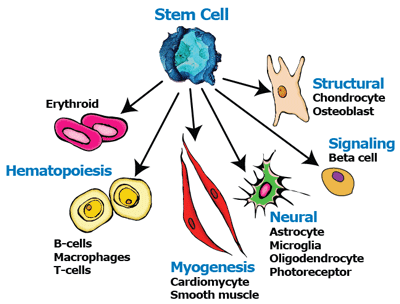
Firstly, studying the mechanisms
and biology of stem cells can provided detailed information into how human
development works. Understanding how undifferentiated cells can develop into
all the different types of cells in the human body can provide information
about certain diseases that occur from abnormal cell differentiation and
division, such as cancer and birth defects. In addition, having a more complete
understanding of these processes can lead to the development of better
treatments and therapies for various diseases.
Human stem cells are also being
used to test the effects of new drugs and pharmaceuticals. The cell lines that
are grown from stem cells can be used to test specific activity of medications,
such as testing a cancer cell line with an anti-tumor drug. The use of stem
cells would allow for the testing of a vast variety of cell types and allow for
the development of more efficient treatments and cures without risking the
lives of test subjects. Of course, this process is not as easy as it seems.
Scientists must be able to control the settings and conditions of the stem
cells to be identical for each drug test; otherwise, the experiment becomes
corrupted with other variables and can lead to inaccurate results. Lack of full
understanding of certain cell pathways and mechanisms makes controlling every
aspect of a cell’s components and environment a daunting task.
The most important application of
stem cells is the potential to grow complete sets of tissues and organs in the
laboratory from stem cells. While many people donate their organs after they
die, the demand far outweighs the supply. In addition, the risk of rejection of
the transplanted organ is a significant problem that many times creates an
obstacle for helping patients who need the transplant. Thus, by utilizing the
abilities of stem cells to differentiate into any type of cell, transplanting
organs could become a widely available and safe procedure.
Link for this discussion:
National Institute of Health
I have read many articles like this one. And I have to say that stem cells such as Pluripotent Stem Cell is playing a very important role in researches and human health.
ReplyDelete